PRIMARY AND SECONDARY PLANT GROWTH Page
3

<
Page 2
-
II. Secondary Growth
-
B. Cork Cambium
-

-
1. Origin is discontinuous
in space and time
-
a. Initial Cork Cambium derived
from Epidermis or Cortex
-
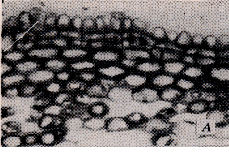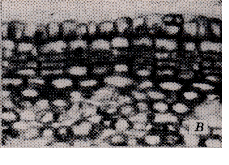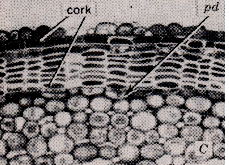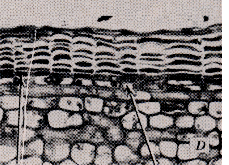
-
b. New Cork Cambium made
each year to inside of old Cork Cambium
-
c. Subsequent Cork Cambium
derived from parenchyma in Primary and Secondary Phloem
-
2. Cork Cambium makes Cork
Cells toward outside
-
3. Because of discontinuity
Bark can include:
-
a. Epidermis + Cortex
-
b. Non Functional Primary
Phloem
-
c. Non Functional Secondary
Phloem
-
4. Can be sloughed off, or
accumulated into thick ridges & furrows
-

-
5. Special regions of loose
cork cells (Lenticels) are produced to facilitate gaseous exchange from
atmosphere to internal living cells.
-

-
6. Human uses of Bark
-
a. Source of Tannic
Acid used in making leather
-
b. Source of Cinnamon,
one of the oldest and most valuable spices known
-
c. Phloem Fibers from
-
1. Flax used to make Linen
cloth
-
2. Hemp used to make Hemp
cloth, canvas, cordage
-
3. Jute used to make Burlap
-
d. Landscape Mulch
-
e. Fuel
-
Page 1
2



