Botany 155 Sec A __Field Botany__ First Written Exam (100 pts).
Name ________________________
|
1. (9 points) Provide the names for the indicated
structures on the plant diagram. A.___Roots___________ B.___Shoot___________ C.___Leaf____________ D.___Axillary Bud____ E.___Node____________ F.___Internode_______ G.____Flower_ H.____Seed___________ I._____Fruit_________ |
|
|
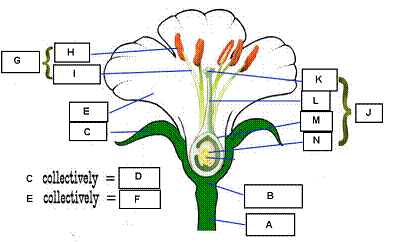
2.
(14
points) Provide the names for the indicated structures on the
flower diagram. A.__pedicel__B.___receptacle_ C.___sepal_____D.__calyx_______ E.___petal____F.___corolla____ G.__stamen_H.___anther_____ I.__filament____J.__carpel______ K.___stigma____L.___style______ M.__ovary______N.__ovule_______ |
|
3. (2 points) Is the leaf in the plant diagram
above a simple or compound leaf? Explain
your answer.
Compound,
because
there are
multiple pinnately arranged leaflets above the axillary bud which
defines the
node.
Fill in the blanks with appropriate terms (14 pts):
4. A tall perennial woody plant having a main trunk and branches forming a distinct elevated crown is called a/an _____tree_________.
5. A plant lacking a permanent woody stem is called a/an _wildflower/herb.
6. A plant with a weak stem that derives support from climbing, twining, or creeping along a surface is called a/an __vine__________.
7. A woody plant smaller than a tree, and usually with several stems from the same base is called a/an ____shrub_______.
8. In a hypogenous flower, the ovary is in a/an _superior_________ position compared to the other parts of the flower.
9. In an epigynous flower, the ovary is in a/an ___inferior__________ position compared to the other parts of the flower.
10. A/an __spike________ is an elongate, unbranched, indeterminate inflorescence with sessile flowers.
11. A/an ___raceme_____ is an elongate, unbranched, indeterminate inflorescence with pedicelled flowers.
12. A/an __panicle______ is a branched raceme.
13. A/an __head/capitulum is a dense vertically compressed inflorescence with sessile flowers on a receptacle and subtended by an involucre of phyllaries, characteristic of the Asteraceae.
14. A/an __fruit________ develops from the ovary wall after fertilization of the egg in the ovule.
15. A/an __seed_________ develops from the ovule after fertilization of the egg in the ovule.
16. _Simple________fruits develop from a single ripened ovary from a single flower.
17.
Aggregate______fruits
develop from a cluster or aggregation of many ripened ovaries (fruits)
produced
from a single flower.
Provide short concise answers to each of the following questions (62 pts):
18. (6
pts) Describe what the terms “pinnate” and
“palmate” mean, and give two examples of leaf characters that might be
modified
by these adjectives.
PINNATE = ARRANGED LIKE PINNA ON A FEATHER. PALMATE = ARRANGED LIKE FINGERS OFF A PALM. USED TO MODIFY LEAF VENATION AND LOBING PATTERNS.
19. (6
pts) Describe the process of using a
dichotomous key to identify an unknown object (like a tree species). Make sure you use the term “couplet” in your
answer.
READ BOTH PARTS OF FIRST COUPLET AND DECIDE WHICH GROUP OF CHARACTER STATES BEST FITS YOUR SPECIMEN. EITHER LEARN THE IDENTITY OF YOUR UNKNOWN, OR BE DIRECTED TO THE NEXT INDICATED COUPLET. REPEAT UNTIL THE IDENTITY OF YOUR UNKNOWN IS REVEALED.
20. (6
pts) Describe and define three character
states one might observe in leaf arrangement.
ALTERNATE= ONE LEAF PER NODE, 137.5 DEGREES BETWEEN SUCCESSIVE NODES..
OPPOSITE = TWO LEAVES PER NODE, 180 DEGREES APART FROM ONE ANOTHER, 90 DEGREES BETWEEN SUCCESSIVE NODES.
WHORLED = MORE THAN 2 LEAVES PER NODE. 360 DEGREES / NUMBER OF LEAVES = ANGLE BETWEEN LEAVES.
21.
(6
pts) Distinquish
between a leaf base and a leaf apex. How are
the
character states associated with each of these leaf parts similar to
each
other?
APEX=
TIP OF LEAF FARTHEST FROM PETIOLE. BASE =
PART OF LEAF WHERE BLADE JOINS THE PETIOLE. CHARACTER STATES
ASSOCIATED
WITH BOTH APEX AND SHAPE REFER TO THEIR
GEOMETIRC
SHAPES.
22.
(6
pts) Explain
how an imperfect flower necessarily has to be an incomplete flower, but
that an
incomplete flower does not necessarily mean that it is imperfect.
INCOMPLETE REFERS TO FLOWERS THAT ARE MISSING AT LEAST ONE OF THE FOUR FLORAL ORGANS, WHEREAS, IMPERFECT REFERS TO FLOWERS THAT ARE MISSING EITHER THE STAMENS OR PISTILS, SO IF A FLOWER IS MISSING EITHER PETALS OR SEPALS IT WILL BE INCOMPLETE, BUT NOT IMPERFECT.
23. (4
pts) What does pollination
mean?
TRANSFER OF POLLEN FROM ANTHER OF
STAMEN TO STIGMA OF CARPEL.
24. (4 pts) How is the process of fertilization the same in plant and animals?
IN
BOTH
PLANTS AND ANIMALS FERTILIZATION REFERS
TO THE FUSION OF A SPERM WITH AN EGG (BOTH HAPLOID) TO FORM A DIPLOID
ZYGOTE.
25. (4
pts) What is
different between the way gametes (egg and sperm cells) are produced in
plants
compared to animals?
IN
ANIMALS
GAMETES ARE PRODUCED BY MEIOSIS,
WHEREAS IN PLANTS THEY ARE PRODUCED BY MITOSIS OF SPECIALIZED CELLS IN
THE
HAPLOID GAMETOPHYTE GENERATION.
26. (4 pts) What does double fertilization in angiosperms mean?
ONE
SPERM
FUSES WITH THE EGG TO FORM THE
ZYGOTE, THE OTHER SPERM FUSES WITH THE POLAR NUCLEI TO FORM THE
ENDOSPERM.
27. (6
pts) Why are bees important to humans?
THEY
POLLINATE APPROXIMATELY 2/3 OF ALL THE FLOWERS
THAT PRODUCE FRUIT THAT WE EAT IN SOME FORM OR OTHER. IF THERE
WERE NO
BEES, OUR DIET WOULD CONSISTS MOSTLY OF WIND POLLINATED FRUITS (GRASSES
AND
MOST NUTS).
28. (4 pts) What’s the difference between a regular (actinomorphic) and an irregular (zygomorphic) flower?
REGULAR
FLOWERS
ARE RADIALLY
SYMMETRICAL. IRREGULAR FLOWERS ARE BILATERALLY SYMMETRICAL.
29. (4 pts) What’s the differences between a berry and a drupe?
A
DRUPE HAS A STONY ENDOCARP SURROUNDING A
SINGLE SEED. A
30. (4 pts) What’s the difference between a dry dehiscent fruit and a dry indehiscent fruit?
AN
INDEHISCENT FRUIT DOES NOT HAVE REGULAR LINES
ALONG WHICH THE FRUIT BREAKS APART TO RELEASE THE SEEDS,
WHEREAS DEHISCENT FRUITS HAVE ONE OR MORE REGULAR LINES ALONG
WHICH THE
FRUIT SPLITS TO RELEASE THE SEEDS.